Topic 3: Modelling and optimisation to control additive and subtractive manufacturing processes
Keywords: laser powder bed fusion (LPBF), concentrated energy deposition (WAAM, WLAM), 5-axis machining, CAD/CAM, in-situ / in-process instrumentation, real-time control, digital twin
Actors : Olivier Bruneau, Kevin Godineau, Sylvain Lavernhe, Nicolas Muller, Yann Quinsat, Christophe Tournier
Additive manufacturing
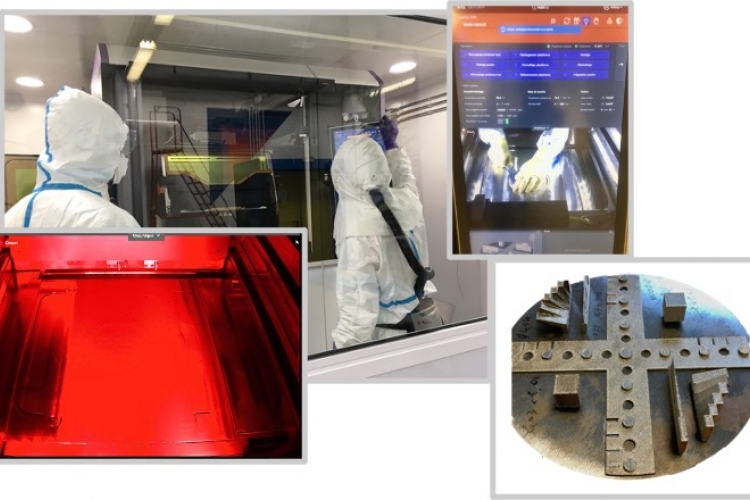
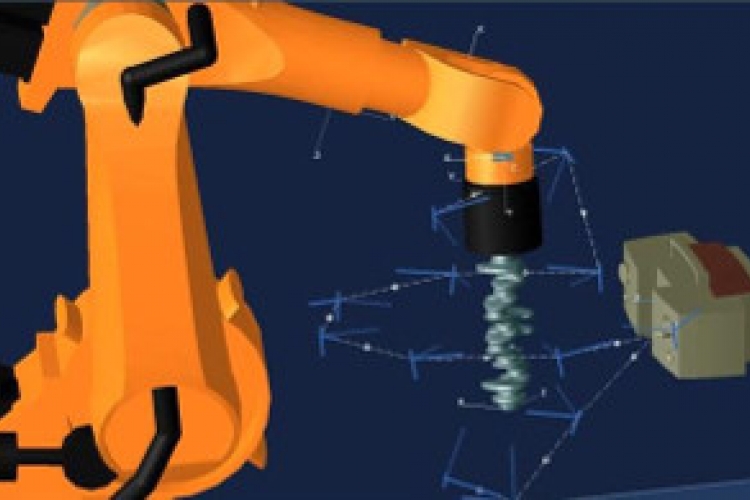
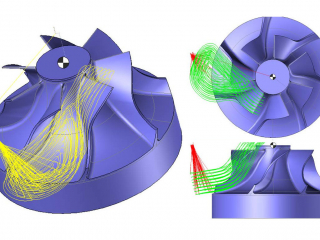
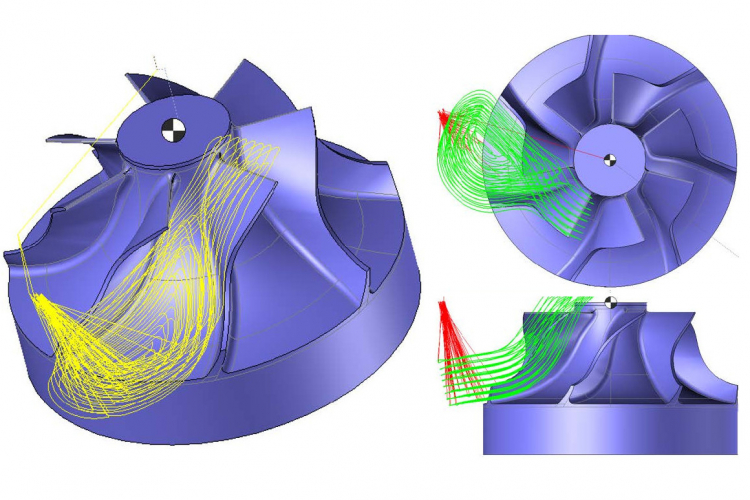
The laboratory's activities in additive manufacturing focus on high-energy processes such as laser powder bed fusion and concentrated energy material deposition. They concern in particular the calculation of 8-axis material deposition trajectories as well as the optimisation of process parameters (laser power, geometric uncertainties and scanning speed, etc.), trajectories and their execution in order to control material health and microstructure and to produce near net shape geometries.
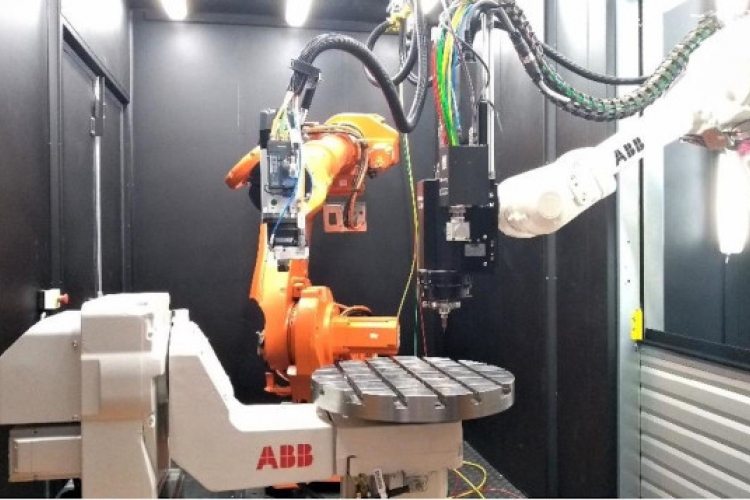
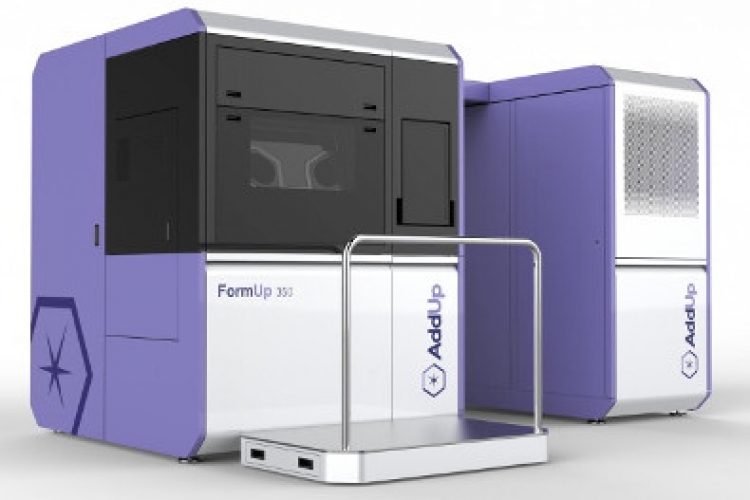
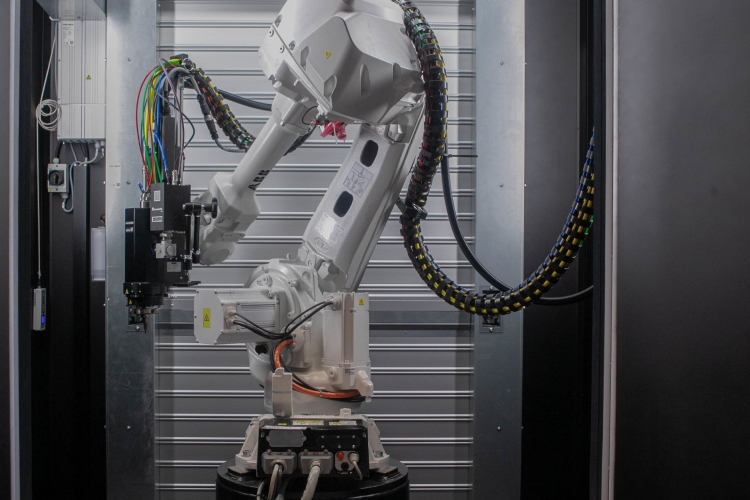
This work is mainly based on the experimental platforms of the laboratory and its partners, i.e. the laser powder bed fusion additive manufacturing machine (FormUp350) and its instrumented control bench, the hybrid additive (wire laser) and subtractive (milling) robotic cell, the WAAM cell of the Additive Factory Hub industrial platform and the Paris-Saclay additive manufacturing initiative partner laboratories resources
Multi-axis machining
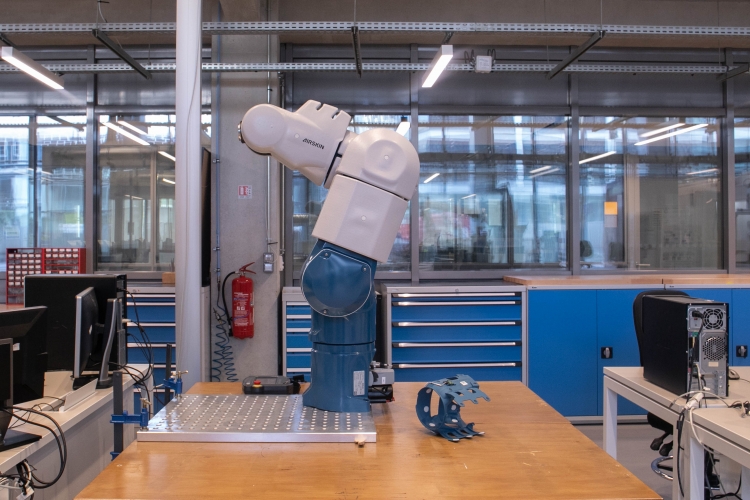
In high-speed multi-axis machining, the work focuses on the optimisation of the steps in the manufacturing process and in particular the machining paths and the control. It is based on the modelling of the process and the articulated mechanical structure from a geometric, kinematic and dynamic point of view. The experimental campaigns are based on the Mikron UCP710 and DMG HSC75 high-speed machining centres as well as on the open numerical control developed in the laboratory.
Simulation models and methods, software prototypes
The laboratory develops models, simulation methods and software prototypes, based on experimental manipulations. The optimisation of the control of manufacturing resources is supported by the exploitation of multi-physical models on the one hand and the integration and development of multi-sensor/multi-scale in-situ measurement techniques to implement data-driven approaches on the other. All of these models and data enable us to develop the building blocks of digital twins for parts, production systems and processes. This work takes the form of national and international academic and industrial partnerships (AddUp, Missler Software, Safran, IRT SystemX, Dassault Systèmes, etc.).
Associated research projects
- GIS HEAD : Groupement d’intérêt scientifique – hautes énergies en fabrication additive
- SOFIA : Solution pour la fabrication industrielle additive métallique
- AFH : Additive Factory Hub
- FAPS : Fabrication Additive Paris-Saclay
- AWESOME : Development of manufacturing strategies by hybridizing WXAM process and 5 axis machining of complex shapes
- MIFASOL : Microstructure on demand in additive manufacturing through a synergy between control, measurements and simulations
- INTEGRATION : Identification traçable d’exactitude géométrique d’axes de rotation - Développement d’un nouvel étalon matériel sans contact
- COLUMBO : Multiscale characterization and controllability by laser-ultrasounds of WLAM components: toward a physics-based and machine learning enhanced online monitoring
- ORACLE : Optimisation de l'interpolation de trajectoires en fabrication additive par fusion laser sur lit de poudre
- SOLARIA : Sources laser & rayonnement pour la fabrication industrielle additive